
Turkey's economy has garnered increased optimism from both the World Bank and the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD). The sentiment in regards to the outlook for the rest of 2023 and into 2024 is largely, conservatively-optimistic. The driving force behind this growth projection is attributed to robust domestic demand, despite challenges related to inflation and post-earthquake reconstruction efforts after the destructive earthquakes in early February.
Macroeconomic Management and Growth
The World Bank's latest Global Economic Prospects report indicates a notable upgrade in Turkey's growth forecast, with an anticipated expansion of 3.2% for this year. This figure is an improvement from the earlier January projection of 2.7%, although it falls short of the remarkable 5.6% growth achieved in 2022. Looking ahead, the World Bank foresees Turkey's economy continuing to gain momentum, with a growth rate of 4.3% anticipated for the following year. Furthermore, their expectations for 2025 are also positive, projecting a growth rate of 4.1%.
Historically, Turkey has benefited from foreign aid and maintained a high rate of investment activity. The World Bank's assistance between 1993 and 2004 focused on macroeconomic management, among other strategic pillars, and the outcomes were rated as moderately satisfactory. The Bank recommends a greater focus on private sector development for Turkey's future economic growth.
OECD Projections and Business Environment
Similarly, the OECD has revised its growth forecast upward, estimating a 3.6% expansion for Turkey's economy in 2023. This new projection surpasses their earlier March estimate of 2.8%, a testament to the economy's resilience and potential. However, the OECD has slightly adjusted its outlook for 2024, now envisioning a growth rate of 3.7%, a minor decrease from the previous 3.8% forecast provided in March.
Turkey's business environment has been historically dominated by state enterprises, large family firms, and small businesses. The country faces the challenge of developing a support system that enables enterprises to leverage their entrepreneurial strengths for growth.

Labor Market and Employment
The Turkish economy is showing signs of easing inflationary pressures that have been a concern over the past few years. Turkey's national job agency training program, ISKUR, supported by the World Bank, offers training in various professions. About 60% of the trainees get hired as permanent employees, indicating a positive outlook for the job market.
Real Estate Market
The momentum driving up Turkish real estate prices remains strong. According to the European Public Real Estate Association (EPRA), the value of Turkey's commercial real estate sector might surpass $300 billion by the close of 2023. The surge in real estate prices, which surged by over 50% between 2020 and 2023, has yielded substantial gains for investors. This trend was further underlined by foreigners investing $5 billion in Turkish real estate during 2022.
Global Real Estate Market Trends and Turkey
The global economy faced challenges stemming from the pandemic, energy shortages, and food supply disruptions. During the most pivotal phases of these crises, substantial investments flowed into the real estate industry. Transforming into a prime avenue for savings, the real estate sector witnessed significant value escalation from 2021 to 2023. Despite an initial decline in global housing growth at the outset of the pandemic, supply-side expenses surged at a pace surpassing previous years. Approaches prioritising health, prompted by the epidemic, gained prominence and influence. As people directed their attention towards real estate investments in locations distant from urban cores, the real estate industry marked its most substantial growth after 2006, coinciding with the resolution of the epidemic. Following a rise of over 15 percent on average between 2020 and 2023, real estate prices persist in their ascending trajectory.
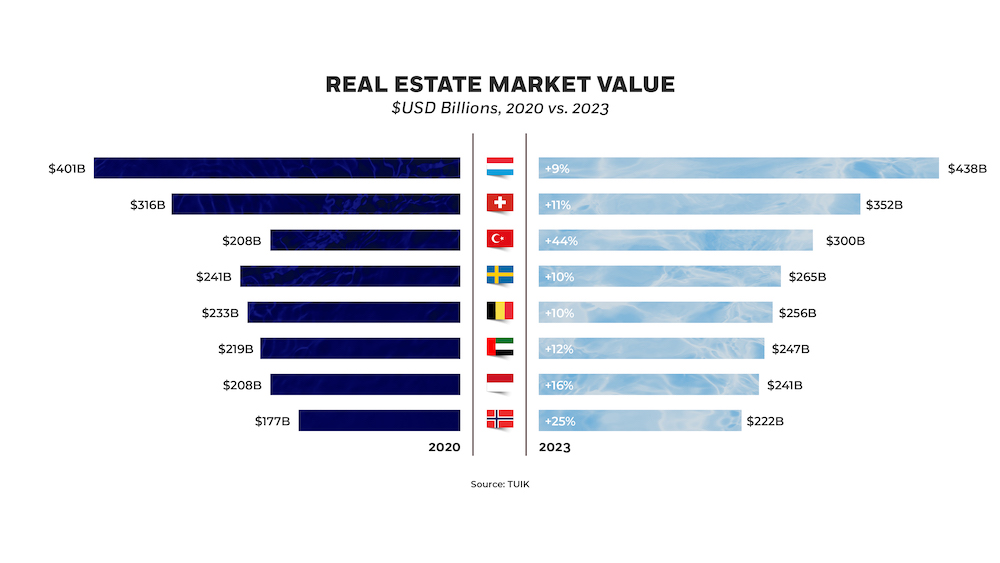
In developed nations like the Netherlands, Switzerland, Sweden, and Belgium, real estate prices witnessed increments below the average; however, in Poland, Norway, and Turkey, they exceeded the average growth. Among these, Turkey, experiencing one of the most significant surges, observed a substantial foreign demand for real estate investments. The global trend of real estate investments has led to the creation of expansive portfolios within pension and mutual funds. Notably, European capital directed toward real estate has been funnelled into developing economies. Within Turkey, which has been influenced by this trend, the collective value of the commercial real estate sector escalated from $208 billion to $300 billion, reflecting an impressive growth rate of 44 percent.
As a broad trend, real estate investments flowing into Turkey tend to concentrate in cities like Istanbul, Antalya, and Mugla. Among these, Istanbul draws the most significant share of real estate investments and holds a prominent position as a hub for tourism. With an annual influx of approximately 16 million tourists, Istanbul emerges as one of the cities with the most dynamic real estate sectors.
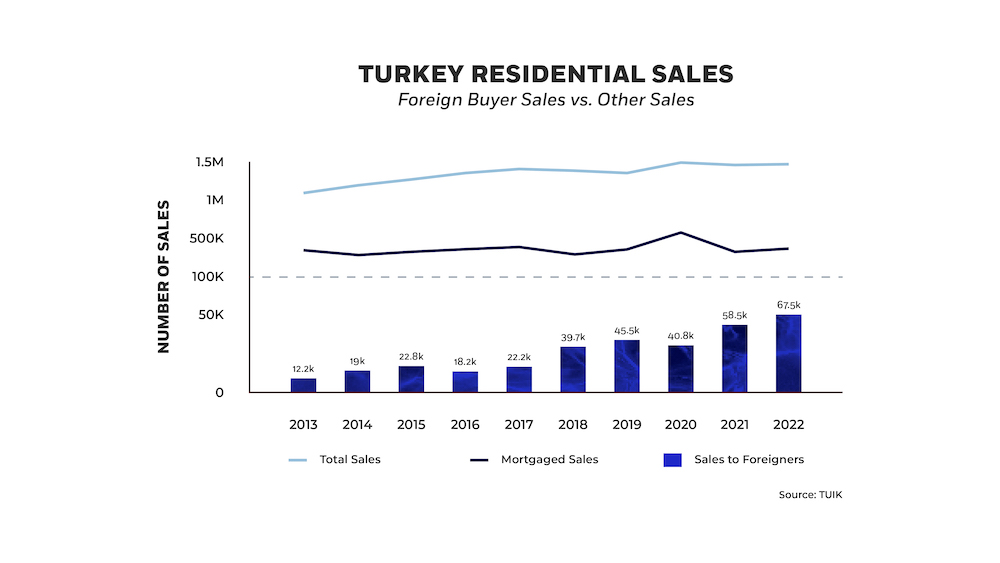
From 2008 to 2022, the yearly volume of house sales in Turkey surged by over threefold, ascending from 427,000 to 1.5 million transactions. A comparable expansion was observable in the realm of foreign property acquisitions. The figure for foreign property purchases, which started at 67,000 in 2008, illustrates the worldwide allure of Turkey's real estate market. Over the aforementioned period, a cumulative total of 380,000 residences were procured by foreign buyers, contributing to an estimated present portfolio valued at over $50 billion.
Future Prospects and Investments
With the appointment of Mehmet Simsek as the head of Finance Bank, Turkey has reoriented itself towards rational economic strategies. This shift is anticipated to make the country even more appealing to potential investors. Projections suggest that Turkey is targeting an influx of $15 billion in foreign investments for the present year, as it endeavours to recover from the aftermath of the recent earthquake. A key focal point for Turkey's economic agenda is urban transformation. Istanbul, in particular, is poised for significant growth in the real estate sector, as an estimated one million houses are anticipated to undergo transformation. This endeavour is expected to further boost the real estate landscape in the city.
In light of these developments and additional insights from the World Bank, Turkey seems to be entering a phase of economic stability and growth, with the real estate sector playing a pivotal role in attracting investments and driving economic progress.
Urban Transformation in Turkey: A Synopsis
Since its launch in 2012, Turkey's urban transformation initiative has made significant strides in addressing housing and infrastructure challenges. The program has successfully transformed around 3.3 million high-risk houses, enhancing the safety and security of residents. The Housing Development Administration of the Republic of Turkey (TOKİ) has been instrumental in this effort, constructing 1.17 million affordable houses for low- and middle-income citizens. Despite these achievements, the program has faced challenges, including legal complexities that have slowed its pace. The recent earthquake in February has further emphasised the urgency of these transformation efforts.
Heritage and Earthquake Preparedness
Turkey's urban transformation also focuses on the restoration and repurposing of historic buildings, especially in earthquake-prone areas. Istanbul is a key centre for this transformation, where state authorities and major Turkish construction companies are collaboratively working on these projects. Turkey's construction sector has an annual export valuation of approximately $60 billion, making it a global leader in providing convenient services, second only to China.

Global Reach of Turkish Contractors
Turkish construction companies have a global footprint, executing a wide range of projects from Western Asia to Latin America. Their expertise includes constructing towering structures, intricate road networks, resilient bridges, expansive ports, and sprawling airports. This global adaptability highlights their proficiency in crafting urban infrastructures that are both functional and aesthetically appealing.
The Path Ahead
Turkey's urban transformation program aims to blend its rich historical heritage with modern construction innovation. The focus on revitalising ancient structures in earthquake-prone regions showcases a fusion of traditional architectural wisdom with cutting-edge engineering. As Turkey continues to export its services globally, it solidifies its position as a pivotal player in urban transformation, merging innovation, resilience, and tradition.








